Logging¶
Handler¶
Handler is a special base class defining what will happen when a
LogRecord is captured. You can initialize and add multiple handlers to
a logger. There are many built-in Handlers such as ConsoleHandler,
which prints LogRecords to the console or FileHandler, which appends
log records to a file.
How to Add Handler¶
TelegramHandler is a handler that takes LogRecord and sends it to a
chat. You can initialize it as below:
from tglogger.handler import TelegramHandler
import logging
handler = TelegramHandler(
level=logging.ERROR, # default value
bot_token="foo",
receiver="bar"
)
# then add handler to logger
logger.addHandler(handler)
Tip
You can also set TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN and TELEGRAM_RECEIVER
environment variables instead of manually adding bot_token and
receiver to TelegramHandler initialization.
Formatter¶
Formatter is a special base class generating a log message from a
LogRecord.
How to Set Formatter¶
TelegramFormatter is a formatter that takes LogRecord
and generates a message specific to Telegram.
from tglogger.formatter import TelegramFormatter
formatter = TelegramFormatter()
# set formatter on handler
handler.setFormatter(formatter)
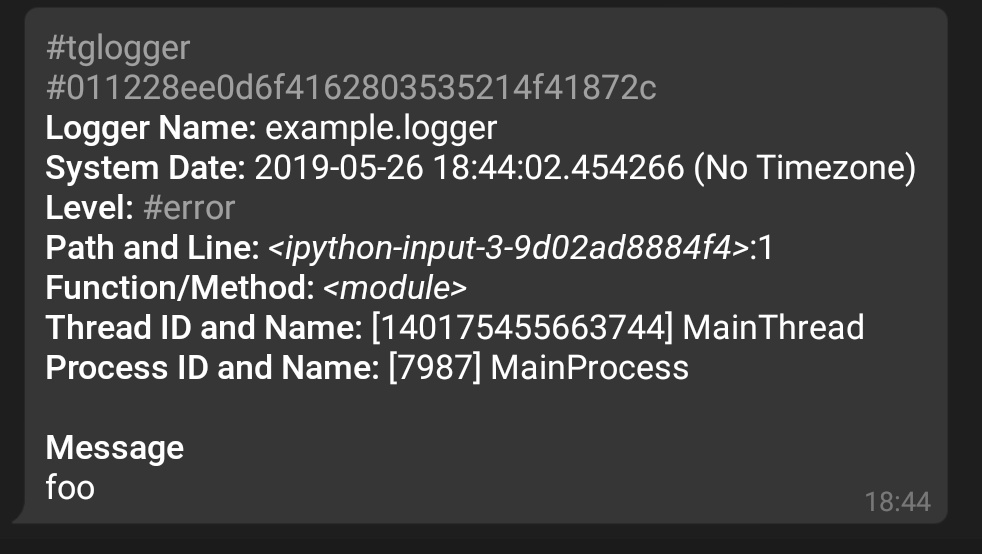
The Message Format¶
The message format is as below:
#tglogger
#{uuid_hex}
*Logger Name:* {logger_name}
*System Date:* {system_date} ({zone})
*Level:* #{level_name}
*Path and Line:* _{path}_:{lineno}
*Function/Method:* _{func_name}_
*Thread ID and Name:* [{thread_id}] {thread_name}
*Process ID and Name:* [{process_id}] {process_name}
*Message*
{message}
- Banner Hashtag (#tglogger): Each message has
#tgloggerbanner hashtag so that you can filter only log messages in a chat. - uuid_hex: It is a unique ID of a
LogRecord. This is especially useful when you want to filter aLogRecord's general info and stack trace message. - logger_name: The name of the logger where the
LogRecordis received from. - system_date: The date of the system. It uses
django.utils.timezoneifDJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULEenvironment variable is set, or uses standard library if it is not set. - zone: If
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULEis set andUSE_TZisTrue, theTIME_ZONEis shown, else it just shows "No Timezone". - level_name: It is a hashtag so that you can filter based on log
level of
LogRecord. - path: The Python file absolute path where the
LogRecordis captured. - line: The line where the
LogRecordis captured. - func_name: The function or method where the
LogRecordis captured. - thread_id: The ID of the thread.
- thread_name: The name of the thread.
- process_id: The ID of the process.
- process_name: The name of the process.
General Setup¶
General Setup consists of the steps below:
- Grab a
logging.Loggerinstance. - Create a
tglogger.handler.TelegramHandlerinstance. - Create a
tglogger.handler.TelegramFormatterinstance. - Set formatter of the
TelegramHandlerinstance. - Add handler to the
Loggerinstance.
An implementation for general purpose is as below:
import logging
from tglogger.handler import TelegramHandler
from tglogger.formatter import TelegramFormatter
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # (1)
# you already have TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN and TELEGRAM_RECEIVER environment variables
handler = TelegramHandler() # (2)
formatter = TelegramFormatter() # (3)
handler.setFormatter(formatter) # (4)
logger.addHandler(handler) # (5)
Sending Logs¶
Regular Logs¶
Any level above ERROR will be sent to chat.
logger.error("foo")
logger.info("bar") # no message will be sent
You can change this behavior by setting level of your handler on initialization or later on.
# after creation
handler.setLevel(logging.INFO) # info and above
# or when you create
handler = TelegramHandler(level=logging.INFO)
Warning
You might want to check bot request throttling on Telegram.
Log Messages with Meta Info¶
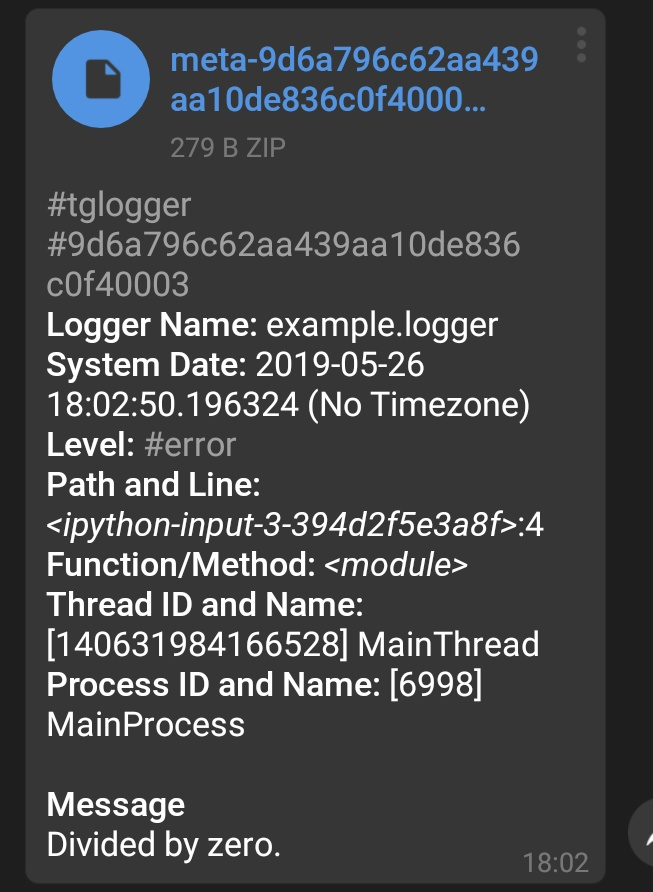
In some occasions, tglogger sends a zip file attached to the message. This
zip file is generated when an exception is captured or DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE
is set.
This generated zip file, for now, only contains stack trace about exception. However, it is planned to contain information about Django settings and request information as well.
Normally, logger captures the exception under an except block as below:
try:
1 / 0 # cannot divide by 0, will fail
except ZeroDivisionError:
logger.exception("Divided by zero.") # or any message you'd like
# as you can see, we do not pass either instance or class of ZeroDivisionError
# logger obtains it itself
Then we receive meta zip as attached to a log message.
Note
Capturing exception behavior is wrapped in Django. If your Django application raises Exception on runtime, you will receive stacktrace.